The initial treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia is medications. However, medications are not as effective for glossopharyngeal neuralgia as they are for
trigeminal neuralgia. As a result, most patients require microvascular decompression (MVD) which is the only advisable surgical procedure. A minimally invasive keyhole approach for microvascular decompression (MVD) will allow your Orange County neurosurgeon Robert Louis, MD to move or separate the blood vessel and hold it away from the irritated glossopharyngeal nerve and the upper two branches of the vagus nerve. MVD is performed using an endoscopic retromastoid approach to create a small quarter-sized bony opening behind the ear.
Minimally Invasive Keyhole Approach
Robert Louis, MD performs this operation is performed through a quarter-sized bony opening using endoscopic techniques. This keyhole approach preserves the surrounding normal structures as best as possible. Depending on the nerve affected, various other therapies may be indicated. By incorporating cutting-edge technology and instrumentation with proven surgical experience, we make surgery safer, less invasive, and more effective. Learn more about cranial nerve disorders.
Robert Louis, MD specializes in minimally invasive removal of chordoma. Less invasive keyhole surgical approaches incorporate Dr. Louis’ experience and education with cutting-edge technology and instrumentation.
Retomastoid Approach – Facial nerves and blood vessels may be approached directly using the Retromastoid Approach. Robert Louis, MD specializes in this state-of-the-art, minimally invasive keyhole approach to accessing cranial nerves and blood vessels through a small bony opening behind the ear. This approach incorporates cutting-edge technology and instrumentation with Dr. Louis’s surgical experience and training, making surgery safer, less invasive, and more effective. Read more about Retromastoid Approach.
Ablation Therapy
Ablation therapy is designed to ablate or selectively destroy specific fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve and spare healthy tissue and lower risk and discomfort for patients. This therapy consists of various approaches to cutting or sectioning the nerve. Ablation therapy is recommended as a last resort.
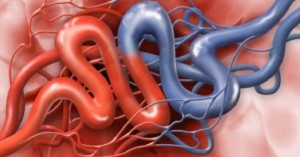 Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a condition caused most frequently by an abnormal looping artery impinging against the Glossopharyngeal nerve, the root entry zone into the brain stem. This cranial nerve condition is similar to trigeminal neuralgia but is much less common. The shooting pain occurs in the throat, tonsil region, and base of the tongue on one side. The pain may be spontaneous and is often triggered by swallowing.
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a condition caused most frequently by an abnormal looping artery impinging against the Glossopharyngeal nerve, the root entry zone into the brain stem. This cranial nerve condition is similar to trigeminal neuralgia but is much less common. The shooting pain occurs in the throat, tonsil region, and base of the tongue on one side. The pain may be spontaneous and is often triggered by swallowing.