Brain surgery is a delicate and risky procedure that is performed on the brain. For this reason, it’s crucial to understand the purpose, types, and risks involved in brain surgery before you have one.
Brain surgery can be done for many different reasons, including removing a tumor or abscess, repairing damage caused by trauma or stroke, alleviating pressure on the brain due to bleeding, and more. We discuss what types of procedures are available for treating problems with your brain and what risks you should consider before going through this surgical procedure.
What Is Brain Surgery?
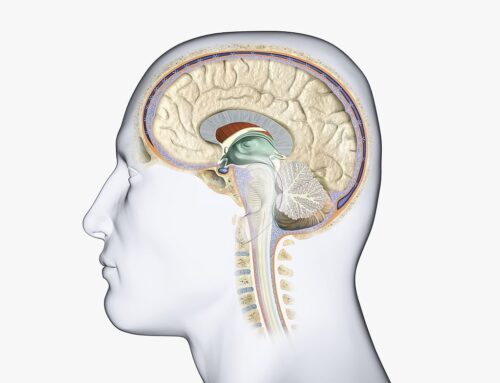
Brain surgery treatment is a surgical procedure that treats problems in the brain. The treatment is performed by a neurosurgeon and involves a physician anesthesiologist who is well versed in anesthesia, how it works on the brain, monitoring, and post-operative care practices after the sensitive procedure.
Who Needs Brain Surgery Treatment?
There are various reasons why a person might need brain surgery treatment. The most common reasons are:
- Tumors
- Hemorrhages (bleeding)
- Strokes
- Aneurysms
- Epilepsy
- Traumatic brain injuries
- Skull fractures
- Blood clots
- Fluid buildup
- Nerve damage
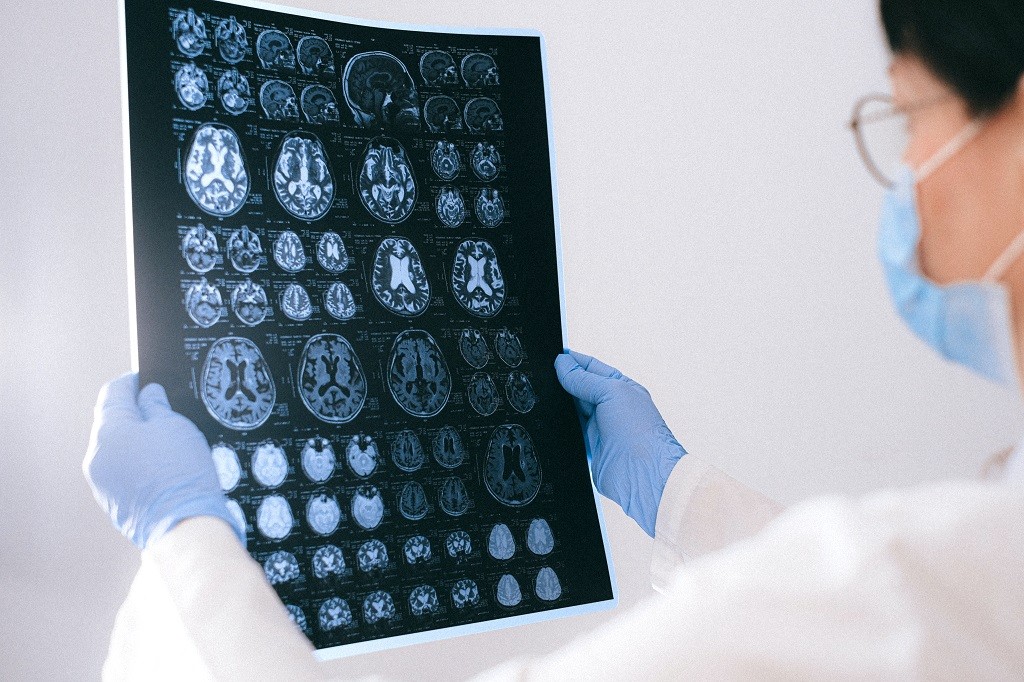
However, before you conclude that your case or a loved one requires brain surgery, you need to come in for a consultation at Neurosurgeon Newport Beach. Our team will take a complete medical history and do a physical examination. We will also order diagnostic tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to understand your problem better and determine the best course of treatment.
Types of Brain Surgery
There are several types of brain surgery treatment. The most common ones include:
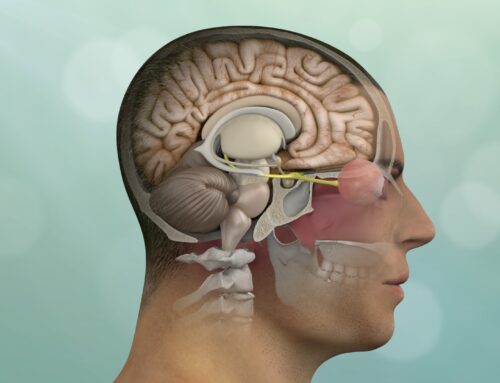
- Craniotomy: This is a type of brain surgery in which the skull and scalp are opened to expose the brain’s surface. It’s done to remove tumors, blood clots, or other growths.
- Biopsy: This is a type of brain surgery in which a small piece of tissue is removed from the brain for examination under a microscope. This type of surgery is used to diagnose tumors, cysts, and other problems.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Involves implanting a device called a stimulator in the brain. The stimulator sends electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain. This type of surgery is used to treat conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremors, and dystonia.
- Laser ablation: This surgical procedure uses a laser beam to destroy abnormal tissue in the brain which may be too deep to access through craniotomy.
- Neuroendoscopy: Involves inserting a small tube with a camera attached to it into the brain. The surgeon uses this device to see inside the brain without making large incisions in the scalp and skull. This type of surgery is used for tumors, vascular diseases, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and other problems that can’t be treated with open surgery.
The surgeon has to take special precautions while performing each of these brain surgeries because the brain controls all of the body’s functions, and any damage can cause paralysis, loss of speech, or even death.
What Happens During Brain Surgery?
Brain surgery is different for each person, depending on the problem being treated. However, some general steps are followed in most brain surgeries:
- The patient is given general anesthesia to make them unconscious and keep them from feeling pain. However, there are cases where a patient is only given local anesthesia, which numbs the area around the surgery, meaning they can still respond to stimuli but won’t feel any pain
- A small hole is drilled in the skull.
- The surgeon uses special tools to cut away the bone and open up the area around the brain.
- The surgeon removes or repairs the damaged tissue.
- The neurosurgeon and his team monitor your brain activity through a functional MRI
- The site is stitched closed, and a bandage is placed over the wound.
After surgery, the patient is observed in the hospital for several days to ensure no complications.
Brain Surgery Treatment Risks
As with any surgery, some risks come with brain surgery. Some of the most common side effects that occur immediately after surgery include:
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Movement or balance problems
- Confusion
- Brain swelling
- Aphasia (difficulty speaking)
There’s also a risk of long-term brain surgery effects such as:
- Infections, such as meningitis or abscesses
- Bleeding in the brain
- A stroke is caused by a hematoma (blood clot) formed near an artery to the brain after surgery.
- Brain damage
- Behavior change
- Memory loss
- Speech problems
- Difficulty walking
- Weakness in the arms and legs
Due to these risks, brain surgery is typically only considered when other treatments have not been successful.
Brain Surgery Treatment Recovery
After brain surgery, a patient may need to stay in the hospital for one to two weeks, and will usually take at least six months before returning full-time to work.
The recovery process depends on which part of the brain was treated and what procedures were used. During this time, it’s crucial to follow the doctor’s instructions carefully and to take them easy.
After surgery, there may be some side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, headaches, and fatigue. These typically go away over time but if they persist or are particularly bothersome, be sure to let your doctor know.
Learn More About Brain Surgery
If you’d like to learn more about brain surgery, be sure to contact us or book a consultation by calling us at (949) 383-4185 with our neurosurgeon Robert Louis MD. We’ll be happy to answer any of your questions and help you make the best decision for your health.