Pituitary Adenoma Newport Beach & Orange County, CA
Pituitary Adenoma Treatment in Orange County
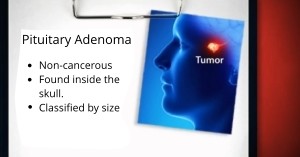 A pituitary adenoma is uncommon and non-cancerous. It is a benign tumor that develops on the pituitary gland, found inside the skull just above the nasal passages. Pituitary cancers are called pituitary carcinomas and are extremely rare. Pituitary adenomas are classified according to size:
A pituitary adenoma is uncommon and non-cancerous. It is a benign tumor that develops on the pituitary gland, found inside the skull just above the nasal passages. Pituitary cancers are called pituitary carcinomas and are extremely rare. Pituitary adenomas are classified according to size:
Microadenomas – are tumors that are smaller than one centimeter across. They rarely press on other tissue, but they can cause symptoms if they release too much of a certain hormone into the bloodstream.
Macroadenomas – are larger than one centimeter across. Macroadenomas can also affect hormone production and they are large enough to press on nearby tissue or nerves, causing damage.
Robert Louis, MD, a fellowship-trained Orange County Neurosurgeon, is the Director of the Skull Base and Pituitary Tumor Program at Hoag Memorial Hospital in Orange County, California. Dr. Louis has particular expertise in the endoscopic and minimally invasive treatment of benign and malignant brain tumors, sellar and parasellar tumors, and skull base tumors.
Dr. Robert Louis specializes in minimally invasive endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for the removal of pituitary tumors. For appointments, please call (949) 383-4185 or Contact Us.