Introduction
Meningioma is a type of brain tumor that arises from the meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Although often benign, meningiomas can still cause serious health complications due to their location and size. In this article, we will explore what meningiomas are, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. We will also discuss the life expectancy for those with benign meningiomas and the role of neurosurgeons in managing this condition.
What is Meningioma?
Meningiomas are the most common primary brain tumors, accounting for about 30% of all cases. They originate from the meningeal cells, which are part of the protective layers of tissue that surround the brain and spinal cord. Meningiomas are typically slow-growing tumors and are classified as benign in the vast majority of cases. However, some meningiomas can be atypical or malignant, posing a higher risk of recurrence and invasion.
There are various types of meningiomas, which are classified based on their appearance under a microscope. The World Health Organization (WHO) has established a grading system to classify meningiomas into three grades: Grade I meningiomas are benign, Grade II are atypical, and Grade III are malignant. The grade of the tumor can influence the treatment approach and prognosis.
Causes of Meningioma
The exact cause of meningioma is still unknown, but some factors may increase the risk of developing this type of brain tumor. These factors include age, as the incidence of meningiomas tends to increase with age; sex, as women are more likely to develop meningiomas than men; and exposure to ionizing radiation.
Certain genetic conditions, such as neurofibromatosis type 2, can also increase the risk of developing meningiomas. However, for most people with meningiomas, there is no known cause or identifiable risk factor.
Meningioma Symptoms
Meningioma symptoms can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor. Many individuals with small meningiomas may not experience any symptoms at all, while others may have a range of neurological issues. Some common symptoms associated with meningiomas include headaches, seizures, vision problems, hearing loss, and weakness or numbness in the limbs.
Other symptoms may include memory loss, difficulty concentrating, personality changes, or difficulties with balance and coordination. It is important to note that these symptoms are not specific to meningiomas and can be caused by various other conditions. Therefore, if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a neurologist Newport Beach or neurosurgeon, for further evaluation.
Meningioma Diagnosis
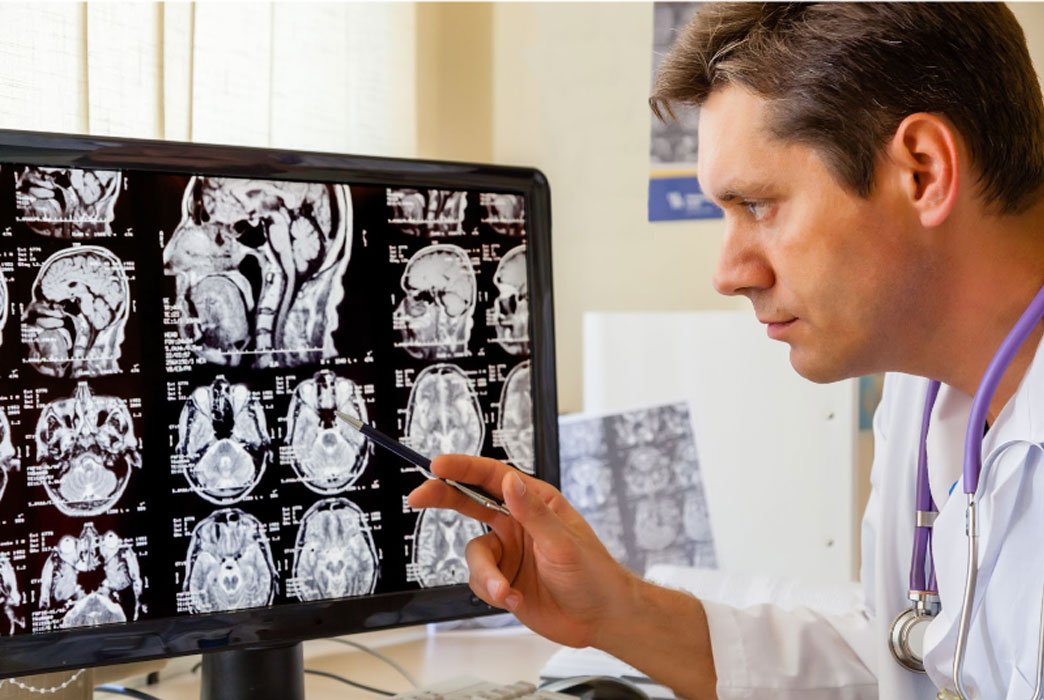
The process of diagnosing a meningioma typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. If a meningioma is suspected, imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans are performed to visualize the tumor and its location within the brain. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the grade of the tumor.
Meningioma Treatment Options
Meningioma treatment Newport Beach & Orange County, CA options depend on several factors, including the size, location, and grade of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences. For small, asymptomatic meningiomas, a “watchful waiting” approach may be recommended, in which the tumor is closely monitored with regular imaging studies but no immediate treatment is pursued.
In cases where treatment is necessary, options include meningioma surgery, radiation therapy, and, in some cases, chemotherapy. Meningioma surgery is often the first line of treatment for accessible tumors and involves the complete or partial removal of the meningioma. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while minimizing damage to surrounding brain tissue. A neurosurgeon, such as one in Newport Beach, Orange County, CA, or at Brain Spine MD., can perform this delicate procedure.
Radiation therapy may be used in conjunction with surgery, especially for atypical or malignant meningiomas or when complete removal of the tumor is not possible. Stereotactic radiosurgery, such as Gamma Knife or CyberKnife, can deliver precise, high-dose radiation to the tumor while minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
Chemotherapy is generally not the first-line treatment for meningiomas, as they tend to be resistant to most chemotherapy drugs. However, in cases where other treatments have been unsuccessful or when the tumor is aggressive or malignant, chemotherapy may be considered.
Benign Meningioma Life Expectancy
The life expectancy for individuals with benign meningiomas is generally favorable, especially if the tumor is completely removed during surgery. In many cases, benign meningiomas do not recur after surgical removal. However, the prognosis can be influenced by factors such as the tumor’s location, size, and the patient’s overall health. Regular follow-up care and monitoring are essential to ensure the tumor does not recur or cause further complications.
Support and Coping Strategies
Coping with a meningioma diagnosis and its potential impact on one’s quality of life can be challenging. It is crucial to have a strong support system in place, including friends, family, and healthcare professionals, like those at Brain Spine M.D. Connecting with others who have experienced similar situations through support groups or online forums can provide valuable insight and emotional support.
The Role of the Neurosurgeon in Meningioma Management
A neurosurgeon Orange County plays a critical role in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of meningiomas. They have specialized training and expertise in performing complex surgeries on the brain and spinal cord. In addition, neurosurgeons can collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as neurologists and radiation oncologists, to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Final Thoughts
Meningiomas are common brain tumors that can cause a range of symptoms depending on their size and location. Although most meningiomas are benign, they can still lead to serious complications if not properly managed. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and, in some cases, chemotherapy. With appropriate care and follow-up, many individuals with meningiomas can expect a favorable prognosis.
It is essential to consult with a Neurosurgeon Newport Beach, CA to discuss your symptoms and receive the most appropriate care for your specific situation. Contact us to schedule an appointment by calling us at (949) 383-4185 today.